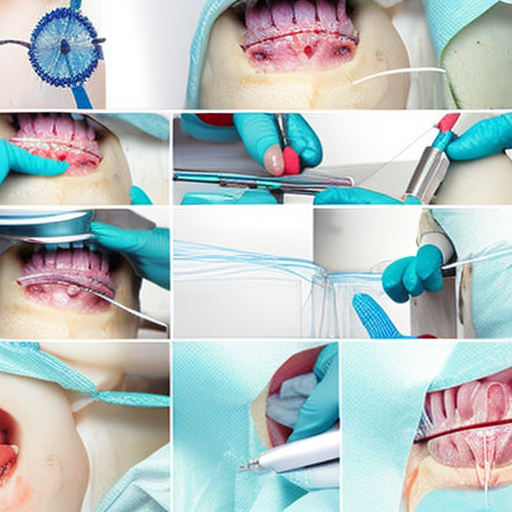
Surgical stitches, also known as sutures, play a crucial role in ensuring proper wound closure and promoting healing after surgical procedures. Different stitch techniques are used depending on the type and location of the wound, as well as the desired outcome. Let’s explore some commonly used stitch techniques in surgical procedures.
1. Interrupted Sutures
Interrupted sutures are widely used in surgery and involve tying individual stitches at regular intervals along the wound edges. This technique provides excellent wound closure, allowing for precise alignment of the tissues. It also offers increased tensile strength and reduces the risk of wound dehiscence (opening) or infections.
2. Continuous Sutures
Continuous sutures, also known as running sutures, involve a single, continuous length of suture material used to stitch the wound. This technique is faster than interrupted sutures and creates a secure closure. However, if one part of the suture breaks, the entire suture line can become loose.
3. Subcuticular Sutures
Subcuticular sutures are placed underneath the skin surface, usually in a horizontal or vertical fashion. This technique provides an excellent cosmetic outcome as the sutures are hidden beneath the epidermis. Subcuticular sutures are commonly used for wound closure in plastic surgery and delicate areas such as the face.
4. Mattress Sutures
Mattress sutures are used when additional wound edge eversion and tension reduction are required. This technique involves passing the suture through deeper tissue layers before coming out through the skin surface. It helps to distribute tension evenly along the wound edges, minimizing the risk of tissue necrosis or scarring.
Summary of :
- Interrupted sutures - precise alignment and increased tensile strength
- Continuous sutures - time-efficient and secure closure
- Subcuticular sutures – excellent cosmetic outcome and hidden sutures
- Mattress sutures – evert wound edges and reduce tension